PARTS OF THE MOTHERBOARD
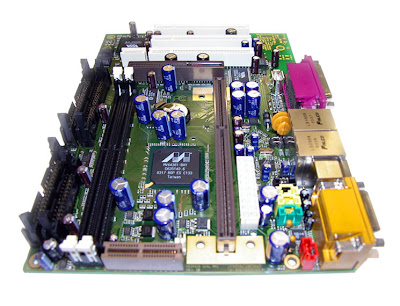
MOTHERBOARD
 AT or ATX? (yes, there are some AT P2 boards). Intel BX, LX, or a non-Intel chipset based board? 5 PCI / 2 ISA or 4 PCI / 3 ISA?
AT or ATX? (yes, there are some AT P2 boards). Intel BX, LX, or a non-Intel chipset based board? 5 PCI / 2 ISA or 4 PCI / 3 ISA?
Overclocking friendly, or stability as the overriding factor?
Those questions notwithstanding, the two most popular BX boards are the Abit BH6 and Asus P2B. That's one person's opinion, and I'm sure you'll hear more. One of the "neater" features of these two boards is the ability to run a 66MHz FSB P2 (eg. P2-300 and P2-333) at the 100MHz FSB setting.
PROCESSOR


Based on revolutionary Intel® Core™ microarchitecture, the breakthrough Intel® Core™2 Duo processor family is designed to provide powerful energy-efficient performance so you can do more at once without slowing down.
With Intel® Core™2 Duo processor, you'll experience revolutionary performance, unbelievable system responsiveness, and energy-efficiency second to none. And, you won't have to slow down for virus scan, multiple compute intensive programs, or multimedia downloads—these desktop processors are up to 40 percent faster with improved energy-efficiency.¹
With Intel Core 2 Duo processors powering your desktop and laptop PCs you'll get the latest arsenal of performance-rich technologies, including up to 4MB of shared L2 cache, up to 1333 MHz front side bus for desktop, and up to 800 MHz front side bus for laptop, you've got the future of computing now, and only from Intel:The Intel Core 2 Duo processor-based desktop PC was designed from the ground up for energy efficiency, letting you enjoy higher performing, ultra-quiet, sleek, and low power desktop PC designs. The Core 2 brand refers to a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit dual-core and MCM quad-core CPUs with the x86-64 instruction set, and based on the Intel Core microarchitecture, which derived from the 32-bit dual-core Yonah laptop processor. (Note: The Yonah had two interconnected cores, similar to those branded as Pentium M, but comprising a single silicon chip or die.) The 2x2 MCM quad-core CPU (dual-die dual-core[1]) had two separate dual-core CPUs (dies) - next to each other - in one quad-core MCM package. The Core 2 relegated the Pentium brand to a lower-end market, and reunified the laptop and desktop CPU lines divided into the Pentium 4, D, and M brands.
The Core microarchitecture returned to lower clock speeds and improved processors' usage of both available clock cycles and power compared with preceding NetBurst of the Pentium 4/D branded CPUs[2]. It translated into more efficient decoding stages, execution units, caches, and buses, etc, reducing the power consumption of Core 2 branded CPUs, while enhancing their processing capacity.
The Core 2 brand was introduced on July 27, 2006[3] comprising of the Solo (single-core), Duo (dual-core), Quad (quad-core), and Extreme (dual- or quad-core CPUs for enthusiasts) branches, as of 2007[4]. The Core 2 branded CPUs include: "Conroe" and "Allendale" (dual-core for higher- and lower-end desktops), "Merom" (dual-core for laptops), "Kentsfield" (quad-core for desktops), and their variants named "Penryn" (dual-core for laptops), "Wolfdale" (dual-core for desktops) and "Yorkfield" (quad-core for desktops). (Note: For the server and workstation "Woodcrest", "Clovertown", and "Tigerton" CPUs see the Xeon brand[5].)
The Core 2 branded processors featured the Virtualization Technology (except T5500 or lower end E4x00), Execute Disable Bit, and SSE3. Their Core microarchitecture introduced also SSSE3, Trusted Execution Technology, Enhanced SpeedStep, and Active Management Technology (iAMT2). With a Thermal Design Power (TDP) of up to only 65 W, the Core 2 dual-core Conroe consumed only half the power of less capable, but also dual-core Pentium D-branded desktop chips[6] with a TDP of up to 130 W[7] (a high TDP requires additional cooling that can be noisy or expensive).
Typically for CPUs, the Core 2 Duo E4000/E6000, Core 2 Quad Q6600, Core 2 Extreme dual-core X6800, and quad-core QX6700 and QX6800 CPUs were affected by bugs, but these were apparently minor
SLOTS



The Peripheral Component Interconnect, or or PCI Standard (in practice almost always shortened to PCI), specifies a computer bus for attaching peripheral devices to a computer motherboard. These devices can take any one of the following forms:
An integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard itself, called a planar device in the PCI specification.
An expansion card that fits into a socket.
The PCI bus is common in modern PCs, where it has displaced ISA and VESA Local Bus as the standard expansion bus, but it also appears in many other computer types. The bus will eventually be succeeded by PCI Express from 2004 and onwards.
The PCI specification covers the physical size of the bus (including wire spacing), electrical characteristics, bus timing, and protocols. The specification can be purchased from the PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG). Version
Card
32-bit, 33MHz (added in Rev. 2.0)
64-bit, 33MHz (added in Rev. 2.0)
32-bit, 66MHz (3.3V only, added in Rev. 2.1)
64-bit, 66MHz (3.3V only, added in Rev. 2.1)
Slot
32-bit, 5V (most common on desktop mainboard)
32-bit, 3.3V (rare)
64-bit, 5V (less common, but can also be found on earlier server mainboard)
64-bit, 3.3V (most common on server mainboard before PCI-X appears) Interrupts
Devices are required to follow a protocol so that the interrupt lines can be shared. The PCI bus includes four interrupt lines, all of which are available to each device. However, they are not wired in parallel as are the other traces. The positions of the interrupt lines rotate between slots, so what appears to one device as the INTA# line is INTB# to the next and INTC# to the next. Single-function devices always use their INTA# for interrupt signaling, so the device load is spread fairly evenly across the four available interrupt lines. This alleviates a common problem with sharing interrupts.
PCI bridges (between two PCI buses) map the four interrupt traces on each of their sides in varying ways. Some bridges use a fixed mapping, and in others it is configurable. In the general case, software cannot determine which interrupt line a device's INTA# pin is connected to across a bridge. The mapping of PCI interrupt lines onto system interrupt lines, through the PCI host bridge, is similarly implementation-dependent. The result is that it can be impossible to determine how a PCI device's interrupts will appear to software. Platform-specific BIOS code is meant to know this, and set a field in each device's configuration space indicating which IRQ it is connected to, but this process is not reliable.
PCI interrupt lines are level-triggered. This was chosen over edge-triggering in order to gain an advantage when servicing a shared interrupt line, and for robustness: edge triggered interrupts are easy to miss. However, this efficiency gain comes at the cost of flexibility, and one interrupting device can block all other devices on the same interrupt line. (See "level-triggered interrupt" for explanation.)
Later revisions of the PCI specification add support for message-signalled interrupts. In this system a device signals its need for service by performing a memory write, rather than by asserting a dedicated line. This alleviates the problem of scarcity of interrupt lines. Even if interrupt vectors are still shared, it does not suffer the sharing problems of level-triggered interrupts. It also resolves the routing problem, because the memory write is not unpredictably modified between device and host. Finally, because the message signaling is in-band, it resolves some synchronization problems that can occur with posted writes and out-of-band interrupt lines.
PCI Express does not have physical interrupt lines at all. It uses message-signalled interrupts exclusively. MEMORY



an electronic memory device; "a memory and the CPU form the central part of a computer to which peripherals are attached"
computer storage, memory board, store, memory, storage
computer, computing device, computing machine, data processor, electronic computer, information processing system - a machine for performing calculations automatically
computer hardware, hardware - (computer science) the mechanical, magnetic, electronic, and electrical components making up a computer system
memory device, storage device - a device that preserves information for retrieval
non-volatile storage, nonvolatile storage - computer storage that is not lost when the power is turned off
fixed storage, read-only memory, read-only storage, ROM - (computer science) memory whose contents can be accessed and read but cannot be changed
real storage - the main memory in a virtual memory system
register - (computer science) memory device that is the part of computer memory that has a specific address and that is used to hold information of a specific kind
scratchpad - (computer science) a high-speed internal memory used for temporary storage of preliminary information
virtual memory, virtual storage - (computer science) memory created by using the hard disk to simulate additional random-access memory; the addressable storage space available to the user of a computer system in which virtual addresses are mapped into real addresses
volatile storage - computer storage that is erased when the power is turned off.